Introduction
Model Author: Jerry Pan
Glaucoma, an eye disease that causes irreversible vision loss, poses a major threat to human health worldwide. It is estimated that by 2020, more than 11 million people worldwide will be blinded by glaucoma. Given its lack of early symptoms, early diagnosis is critical to prevent vision damage.
Model Structure & Data Enhancement
However, the lack of specialized ophthalmologists, especially in remote areas, limits early screening and treatment of glaucoma. To address this problem, this study proposes EyeNet, a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based glaucomatous fundus lesion detection system aimed at assisting physicians in more efficient glaucoma screening.
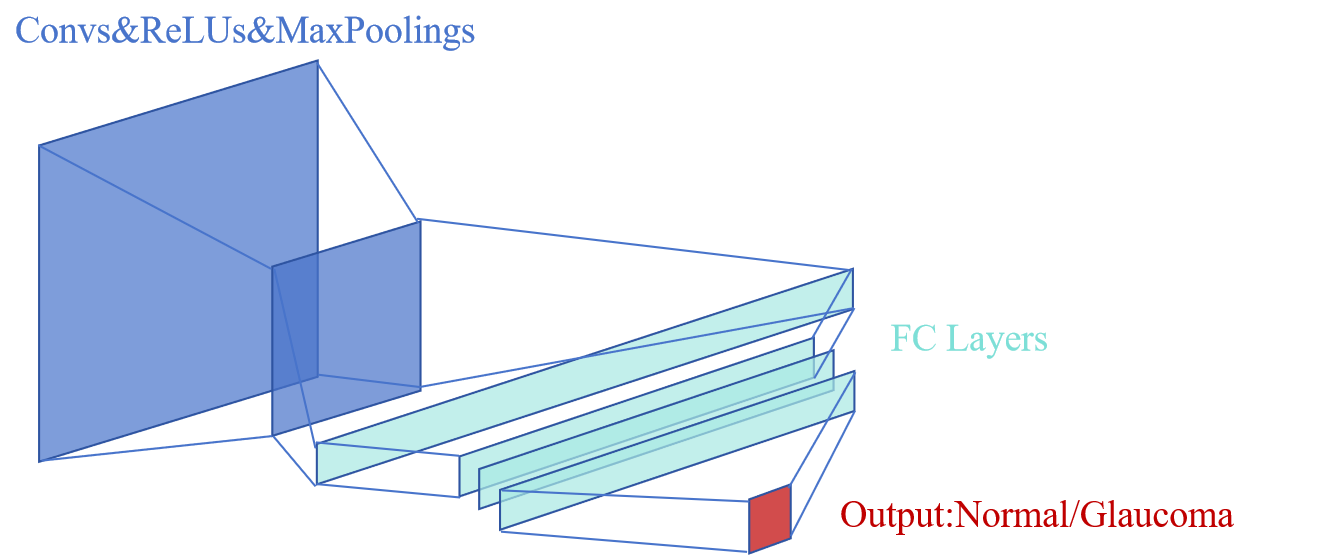
EyeNet Model Structure
Model Training and Accuracy
We utilized the glaucoma fundus lesion image dataset obtained from Kaggle and performed data enhancement via OpenCV to pinpoint the key fundus optic disc regions, which were used as model inputs.
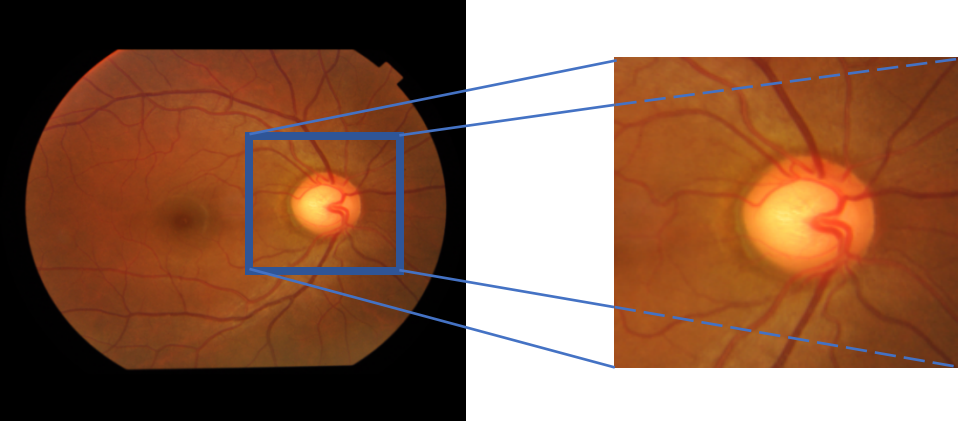
Data Enhancement Illustration
Feature Extraction
The constructed EyeNet model combines multi-layer convolution, pooling, and fully connected layers to extract image features and perform classification. The model was trained using the BCEWithLogitsLoss loss function and the Adam optimizer, and after 140 generations of iterations, EyeNet achieved a high accuracy of 96.59% on the test set.
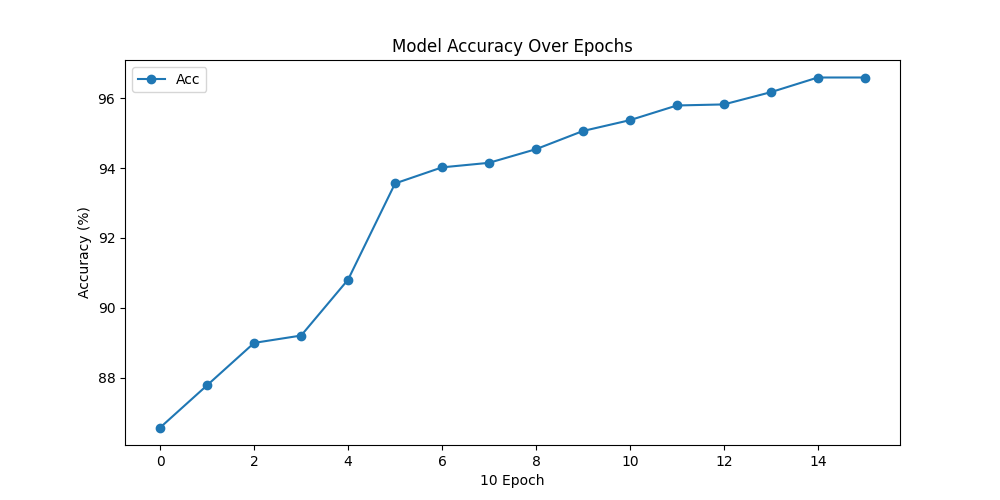
Training Process Accuracy Curve
The team visualized and analyzed the output tensor of each convolutional layer converted into a picture, and found that the model effectively learned the features in the optic nerve, vitreous body, and fundus optic disc, and output the correct result "glaucoma negative".
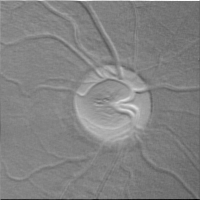
Output of Convolutional Kernel 1 (optic nerve)
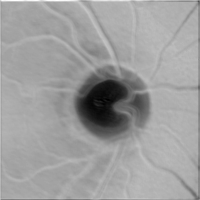
Output of Convolutional Kernel 2 (vitreous body)
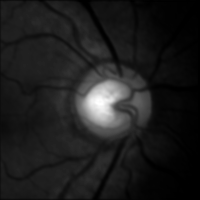
Output of Convolutional Kernel 3 (fundus optic disc)
Innovation and Outlook
The innovation of this study is the application of deep learning techniques to the automated diagnosis of glaucoma, which optimizes the model inputs through data augmentation techniques and significantly improves the training efficiency and diagnostic accuracy. Although the model needs further validation and optimization in practical clinical applications, its potential to improve the early diagnosis rate of glaucoma is obvious, and it is expected to provide effective technical support to alleviate the problem of glaucoma screening in areas with insufficient medical resources.
1. Diversity and balance of datasets
The current model is mainly trained based on specific datasets, and future work needs to be tested on more diverse and balanced datasets to enhance the generalization ability of the model.
2. Model Interpretability
Although CNNs perform well in image recognition, their "black-box" nature limits the model's interpretability. Future research should focus on improving the model's interpretability so that doctors can better understand the model's decision-making process.
3. Multimodal learning
Considering that glaucoma diagnosis may require multiple types of medical images, future research could explore multimodal learning methods that combine fundus images with other types of images (e.g., OCT images).